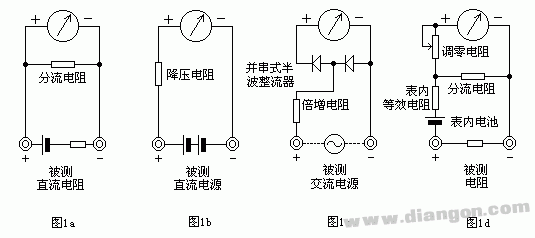
The multimeter is a versatile tool used for measuring various electrical parameters such as voltage, current, and resistance. At its core, it relies on a sensitive magnetic-electric DC ammeter (microampere meter) as the main component. This meter can detect small currents, but it cannot handle large ones directly. Therefore, additional components are used to extend its measurement capabilities.
When measuring **DC current**, the meter is connected in parallel with a shunt resistor. This resistor allows most of the current to bypass the meter, protecting it from damage. By adjusting the value of the shunt resistor, the range of measurable current can be expanded.
For **DC voltage** measurements, a multiplier resistor is connected in series with the meter. This resistor reduces the voltage across the meter, allowing it to measure higher voltages without exceeding its limits. Changing the multiplier resistor’s value adjusts the voltage measurement range.
To measure **AC voltage**, the multimeter uses a rectifier circuit that converts AC into DC. This is necessary because the meter itself only responds to DC. A half-wave or full-wave rectification circuit is typically used, and the method of expanding the AC voltage range is similar to that of DC voltage.
When measuring **resistance**, the multimeter applies a known voltage across the resistor using an internal battery. The current flowing through the resistor is measured, and based on Ohm’s Law, the resistance value is calculated. Shunt resistors are also used here to adjust the measurement range.
Wire Bending Machine,Crimping Tool,Cable Stripping Crimping Machine,Wire Crimping Pliers
Kunshan Bolun Automation Equipment Co., Ltd , https://www.bolunmachinery.com