Developed by non-contact radio frequency identification (RFID), developed by Philips Semiconductors (now NXP Semiconductors), Nokia and Sony, based on RFID and interconnect technology. Near Field Communication (NFC) is a short-range high-frequency radio technology that operates at a distance of 10 cm at 13.56 MHz. The transmission speed is 106 Kbit/s, 212 Kbit/s or 424 Kbit/s. At present, near field communication has passed the ISO/IEC IS 18092 international standard, the ECMA-340 standard and the ETSI TS 102 190 standard. NFC uses both active and passive read modes.
NFC near-field communication technology is evolved from the integration of contactless radio frequency identification (RFID) and interoperability technologies. It combines inductive readers, inductive cards and point-to-point functions on a single chip to be compatible over short distances. The device performs identification and data exchange. The working frequency is 13.56MHz, but users who use this mobile payment solution must replace the special mobile phone. At present, this technology is widely used in Japan and South Korea, and their mobile phones can be used as airport boarding verification, building access keys, traffic cards, credit cards, payment cards, and the like.
Principle of NFC technology
Near Field Communication (NFC), also known as short-range wireless communication, is a short-range high-frequency wireless communication technology that allows non-contact point-to-point data transmission (within ten centimeters) and exchange between electronic devices. data.
This technology evolved from contactless radio frequency identification (RFID) and is backward compatible with RFID. Originally developed by Sony and Philips, it is mainly used to provide M2M (Machine to Machine) communication in handheld devices such as mobile phones. Because near-field communication has natural security, NFC technology is considered to have great application prospects in the field of mobile payment. At the same time, NFC is also compared to the "safe dialogue" between machines by the China Internet of Things School-Enterprise Alliance because of its better security than other wireless communication technologies.
NFC-enabled devices can exchange data in active or passive mode. In passive mode, a device that initiates NFC communication, also known as an NFC originating device (master device), provides an RF field (RF-field) throughout the communication process, which can select one of 106 kbps, 212 kbps, or 424 kbps. Send data to another device. The other device, called the NFC target device (slave device), does not have to generate a radio frequency field, but uses load modulation technology to transmit data back to the initiating device at the same speed. This communication mechanism is compatible with non-contact smart cards based on ISO14443A, MIFARE and FeliCa. Therefore, in passive mode, NFC-initiated devices can detect and connect contactless smart cards or NFC target devices with the same connection and initialization process. .
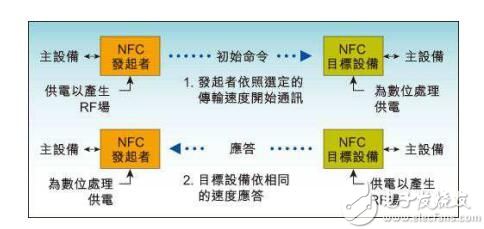
Figure 1: NFC active communication mode
In active mode, each device must generate its own RF field when it wants to send data to another device. As shown in Figure 1, both the initiating device and the target device generate their own RF fields for communication. This is the standard mode for peer-to-peer network communication and allows for very fast connection settings.
Similarities and differences between NFC and RF ID
NFC has the characteristics of two-way connection and identification, working at 13.56MHz frequency, and the working distance is about 10cm. NFC technology promotes standardization under the ISO 18092, ECMA 340 and ETSI TS 102 190 frameworks, and is also compatible with the widely used ISO 14443 Type-A, B and Felica standard contactless smart card infrastructure.
Like RFID, NFC information is also transmitted by electromagnetic induction coupling of the radio frequency portion of the spectrum, but there is still a big difference between the two.
First, NFC is a wireless connection technology that provides easy, secure, and fast communication with a smaller transmission range than RFID. The transmission range of RFID can reach several meters or even tens of meters, but because NFC adopts a unique signal attenuation technology, NFC has the characteristics of close distance, high bandwidth and low energy consumption compared with RFID.
Second, NFC is compatible with existing contactless smart card technology and has become the official standard supported by more and more major vendors.
Once again, NFC is a close-range connection protocol that provides easy, secure, fast, and automatic communication between devices. Compared to other connections in the wireless world, NFC is a close-range, private communication method.
Finally, RFID is more widely used in production, logistics, tracking, and asset management, while NFC plays a huge role in access control, public transportation, and mobile payment.
NFC and Bluetooth difference

Compared with Bluetooth, NFC is suitable for close-range transactions and is suitable for exchanging important information such as financial information or sensitive personal information; Bluetooth is suitable for long-distance data communication. Therefore, NFC and Bluetooth complement each other and coexist. In fact, the fast and lightweight NFC protocol can be used to guide the Bluetooth pairing process between the two devices, simplifying the Bluetooth connection and promoting the use of Bluetooth.
An important application of NFC: mobile payment

NFC technology supports a variety of applications, including mobile payments and transactions, peer-to-peer communications, and mobile information access. The NFC device can be used as a contactless smart card, a smart card reader/writer terminal, and a device-to-device data transmission link. The application can be mainly divided into the following four basic types: for payment and ticket purchase, for electronic ticket, Used for smart media and for exchanging and transmitting data.

The NFC mobile phone has a built-in NFC chip that forms part of the RFID module and can be used as an RFID passive tag—for payment of fees; it can also be used as an RFID reader—for data exchange and acquisition. With NFC phones, people can connect to the entertainment services and transactions they want, from any location, at any time, through any device, to complete payments, get poster information, and more.
64V Battery Pack ,Lithium Battery Box,Lithium Power Pack,Jackery Battery Pack
Zhejiang Casnovo Materials Co., Ltd. , https://www.casnovo-new-energy.com