5G is expected to be commercialized in 2020 and has been widely mentioned. When it comes to 5G, Network Slicing has to be mentioned. As the most discussed technology in 5G, network slicing has great significance for 5G. This article mainly introduces the 5G network slicing technology from the following aspects.

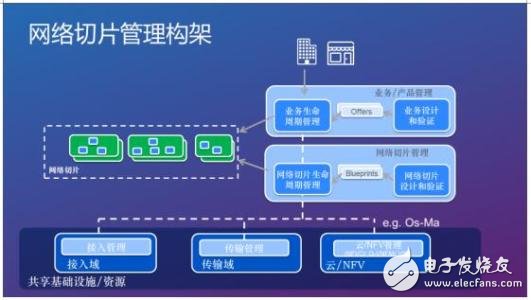
Network slicing can be understood as a set of logical network functions required to support communication services for a particular usage scenario or business model, based on physical infrastructure-to-service implementations that can be viewed as network functions under the EPC ( NetworkFuncTIon) A series of sub-functions (Networksub-FuncTIon) that are decomposed. It can be seen that network slicing is an end-to-end Solution. This end-to-end solution can be applied not only to the core network but also to the radio access network RAN.
Network slices consider the problem from the perspective of the service layer and the infrastructure layer. The service layer describes the system architecture from a logical level, consisting of the links between network functions and functions. These network functions are usually defined in the form of software packages, which provide definitions of deployment and operational requirements (connections, interfaces, KPI requirements, etc.). template. The infrastructure layer describes, at a physical level, the network elements and resources needed to maintain a network slice run, including computing resources (such as IT servers in the data center) and network resources (such as aggregation switches, edge routers, cables, etc.).
After dividing the infrastructure layer and the service layer, you need to consider the mapping problem between the two layers. This is a typical virtual network embedding problem, which mainly includes the following two steps:
1. Mapping from virtual functions to physical functions, including selection of network forwarding elements and computing resources, such as device type and device geographic location selection, the number of required resources is determined by the needs of the service layer.
2. From the virtual link to the physical link mapping, how much physical link bandwidth is allocated depends on the needs of the service layer.
The relationship between any two slices A and B can be one of the following:
Different service layers: For example, slice A provides services for M2M type devices, and slice B provides services for manual operation devices.
Same service layer, but network functionality is slightly modified: for example, slice A supports high mobility users, slice B provides the same service but does not provide mobility support
The same service layer, but different physical applications: For example, both Slice A and Slice B support the same service, but A provides ultra-high confidence and B provides standard confidence, so the deployment requirements of the two slices are different.
Same service layer, same physical application: for example, slices provided for different operators.
Why use network slicing technology in the 5G core network architecture?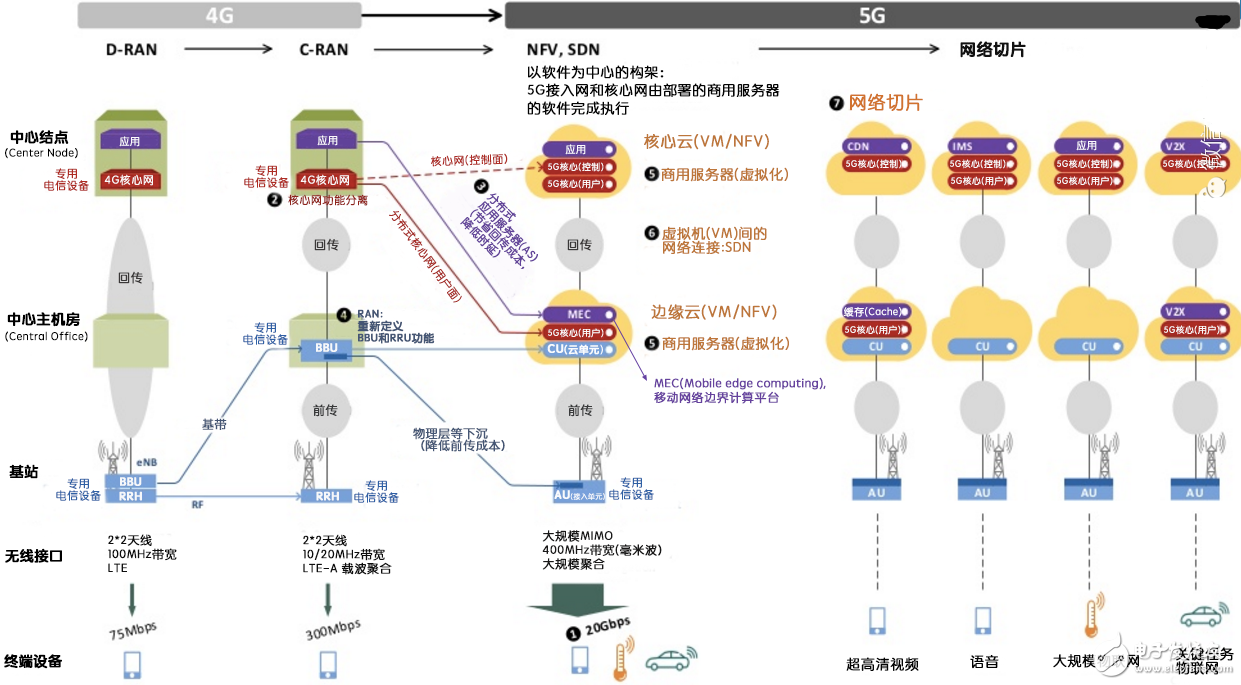
In the 5G era, the object of mobile network services is no longer a simple mobile phone, but various types of devices, such as mobile phones, tablets, fixed sensors, vehicles, and so on. Application scenarios are also diversified, such as mobile broadband, large-scale Internet, mission-critical Internet, and more. The requirements that need to be met are also diverse, such as mobility, security, latency, reliability, and so on. This provides a useful place for network slicing, which cuts out multiple logical networks on a separate physical network through network slicing technology, thus avoiding the construction of a dedicated physical network for each service, which is very cost effective. ! Looking at the network slice described in Figure 1 according to the different needs of different groups, is it easy to understand the value of network slices! From a slicing perspective, the traditional EPC can be considered as a large slice serving all supported mobile devices, but as mentioned earlier, it is not efficient to use a unified network architecture to satisfy all service requests at the same time. Easy to implement, so future networks must transition from "onesizefitsall" to "onesizeperservice" through network slicing technology.
Application scenario classification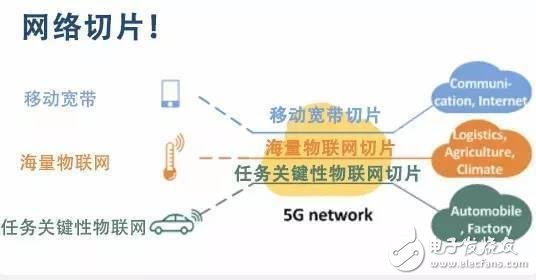
Specifically, 5G networks will address three types of scenarios: mobile broadband, large-scale Internet of Things, and mission-critical IoT. The demand for network services in the three major application scenarios is different:
1, mobile broadband
For 4K/8K ultra-high definition video, holography, augmented reality/virtual reality applications, etc., the network bandwidth and speed requirements are high.
2. Large-scale Internet of Things
Massive IoT sensors are deployed in measurement, construction, agriculture, logistics, smart cities, homes, etc. These sensor devices are very dense, large, and mostly static, with low latency and mobility requirements.
3. Mission-critical Internet of Things
Mainly used in the fields of driverless, car networking, automatic factory, telemedicine, etc., requiring ultra-low latency and high reliability.
To this end, we have to slice the physical network into multiple virtual networks according to different service requirements: smartphone slicing network, autopilot slicing network, large-scale Internet of Things slicing network and so on. ..
What are the challenges of network slicing?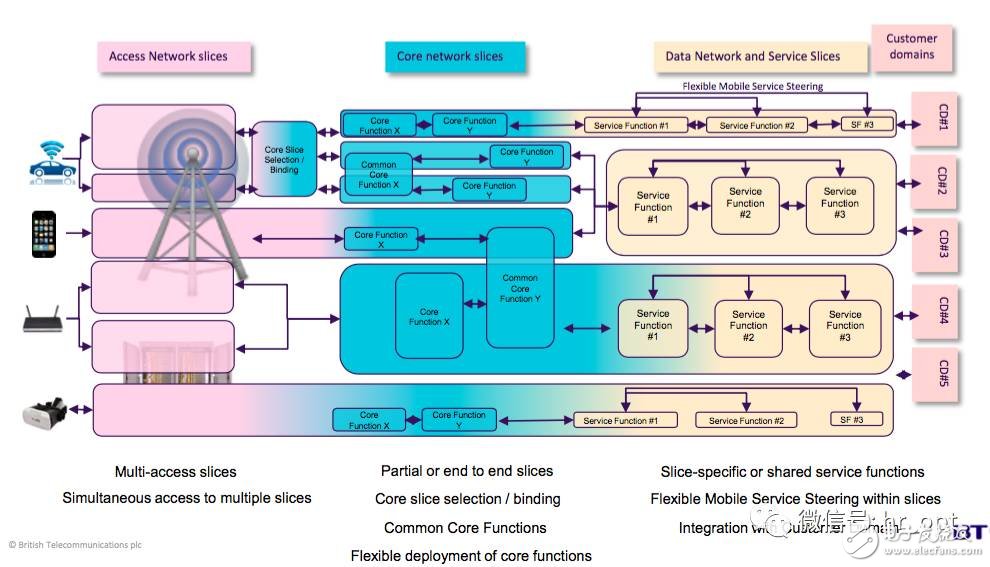
1. Network slice structure: Although eight application scenario series are well defined in Table 1, there are still many unclassified scenarios, so how to determine the granularity of slice partitioning in terms of performance evaluation criteria is still a problem to be solved. problem.
2, network slice selection: a user may use one or more slices, how to choose the right slice is also a basic problem
3. Network slice conversion: In the roaming scenario, the local network slice cannot support the user to access the network, which will cause the user network to be interrupted. One possible solution is to convert the user to the default slice, but how to maintain the IP during the slice conversion process. The connectivity of the session, the task of detecting the timing of the transition should be handed over to the user terminal or to the network, which is still a problem to be solved.
4. User state maintenance: User status information may be transmitted in multiple slices. How to manage user status is also a key issue.
5, the determination of new features: In order to support some new services such as driverless, the current EPC function may not be able to meet, so you need to define new features and the message formats and handlers involved.
to sum upThe diversification of network architecture is an important part of 5G network, and 5G network slicing technology is an indispensable method to realize this diversified architecture. With the continuous development of technologies such as virtualization and network capabilities, the value and significance of network slicing is gradually emerging. Network slicing technology will be an important means for future operators and OTT companies to cooperate backwards, and is an indispensable key technology for operators to achieve new profit models.
Photovoltaic Power Generation Equipment
Photovoltaic Power Generation Equipment,Photovoltaic Power Generation,Solar Photovoltaic Power Generation,Wind Power And Photovoltaic Power Generation
TRANCHART Electrical and Machinery Co.,LTD , https://www.tranchart-electrical.com